Cervical Spine Muscle Energy Technique
Typical Cervical Vertebra (C5-C6)
Diagnosis
Position: Flexed, rotated left, and side-bent left (FRSleft)
Motion Restriction: Extension, right rotation, and right side-bending (ERSright)
The C5 right facet won’t close.
Treatment
Patient is supine on the table with the operator sitting at the head of the table.
Operator’s finger tips of the right index and middle finger are placed on the right articular pillar of C6 to hold the segment so that C5 can be moved upon it.
Operator’s left hand controls the left side of the patient’s head and neck.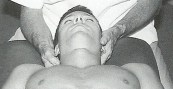
Operator’s right fingers translate the segment anteriorly introducing motion to the backward-bending barrier.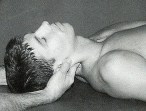
Operator’s left hand introduces right side-bending and rotation of the head and neck to the right by right to left translation engaging the right rotation and the right side-bending barriers.
Patient exerts a small isometric effort against the operator’s resisting left hand into forward bending, left side-bending, or left rotation.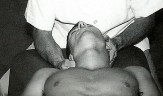
After a 3-5 second muscular effort, the patient relaxes and the operator increases translatory movement in an anterior and right to left direction engaging the backward-bending, right side-bending, and right rotation barriers. This process is repeated 3-5 times.
Retest.



 operator introduces translation from right to left, sensing for resistance to movement at his index fingers. If resistance is felt, the motion restriction is to backward-bending, right side-bending, and right rotation (indicating that the segment is flexed, rotated and side-bent left [FRSleft]). Something has interfered with the capacity of the left facet to close.
operator introduces translation from right to left, sensing for resistance to movement at his index fingers. If resistance is felt, the motion restriction is to backward-bending, right side-bending, and right rotation (indicating that the segment is flexed, rotated and side-bent left [FRSleft]). Something has interfered with the capacity of the left facet to close. operator introduces translation from left to right, sensing for resistance to movement at his index fingers. If resistance is felt, the motion restriction is to backward-bending, left side-bending, and left rotation (indicating that the segment is flexed, rotated, and side-bent right [FRSright]). Something has interfered with the capacity of the right facet to close.
operator introduces translation from left to right, sensing for resistance to movement at his index fingers. If resistance is felt, the motion restriction is to backward-bending, left side-bending, and left rotation (indicating that the segment is flexed, rotated, and side-bent right [FRSright]). Something has interfered with the capacity of the right facet to close.